
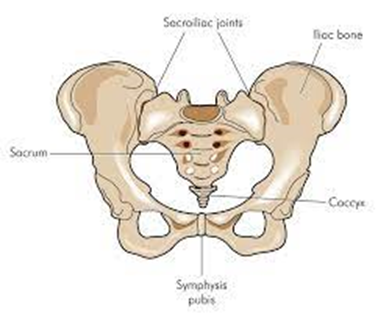
Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) causes inflammation in the joints in your spine. As it progresses, it can affect the sacroiliac joints (the joints which connect the base of your spine and pelvis). This can lead to chronic pain, stiffness, and discomfort in your lower back and hips.
In some people bones in their spine may fuse together, this is known as ‘ankylosis’. This is caused by the body producing extra bits of bone in the spine to heal from the inflammation, which can cause them to fuse together. This can lead to pain and stiffness in your back and neck, and in some rare cases curving of the spine. Fusion of the spine is less common with advances in medical treatment.
Inflammatory back pain, like axSpA is different to back pain caused by straining your back, which may be caused by lifting a heavy object, for example.
What are the symptoms?
Some of the signs of inflammatory back pain include:
- Back pain that lasts more than three months
- Back pain that wakes you up in the middle of the night
- Back pain that gets better with exercise and worse when you are not moving
- Stiffness and pain in your lower back in the morning that lasts for 30 mins or more and then eases throughout the day with movement and activity.
- Pain and stiffness in your buttocks, and sometimes the back of the thighs.
It is important to talk to your GP or rheumatologist if you have these symptoms, as your treatment plan may need to change.
What will happen to me?
There is no cure for axSpA-related inflammatory back pain, but there are many treatments available to help prevent joint damage and manage the symptoms. Your healthcare team can guide you to the right treatment to help prevent joint damage, manage pain, and help you maintain your daily activities.
What can I do?
See a rheumatologist. A rheumatologist can diagnose axSpA and make sure you get the right treatment.
Learn about your condition and play an active role in your treatment. Always talk to your healthcare team about treatments you are thinking about trying. Self-management courses can help you develop skills to be actively involved in your healthcare. Contact your local arthritis office for details of these courses.
Stay active. Regular movement and physical therapy are important to retain flexibility in the spine. A physiotherapist or exercise physiologist can suggest a specific program of exercises suitable for you. It is important to undertake your recommended program regularly. If you experience early morning stiffness, gentle stretching exercises under a warm shower may help. In addition to your regular tailored exercise program for your joints, it is important to do at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week. This is important for your general fitness and also important for the health of your heart and lungs (aerobic fitness). However, not all exercises are suitable for axSpA It is important to speak with your physiotherapist, who will recommend appropriate exercise for your condition. Particularly if you have advanced axSpA and limited movement in your spine.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle. Try to eat a healthy diet, stop smoking, and reduce stress to help your oval health and wellbeing. If you are carrying extra kilos, losing weight with the assistance of a dietitian may help. You may find strategies to help reduce stress and anxiety to be beneficial.
Learn ways to manage pain. Understanding pain and learning techniques that may help you cope with pain are an important part of managing your back pain.
Acknowledge your feelings and seek support. It is natural to feel worried, frustrated, sad and sometimes angry when you have pain. Be aware of these feelings and get help if they start affecting your daily life. A psychologist can help you manage anxiety, fears or worry.
Talk to healthcare team if you are unsure about the things you can do to help manage your back pain.
CONTACT YOUR LOCAL ARTHRITIS OFFICE FOR MORE INFORMATION AND SUPPORT SERVICES.









